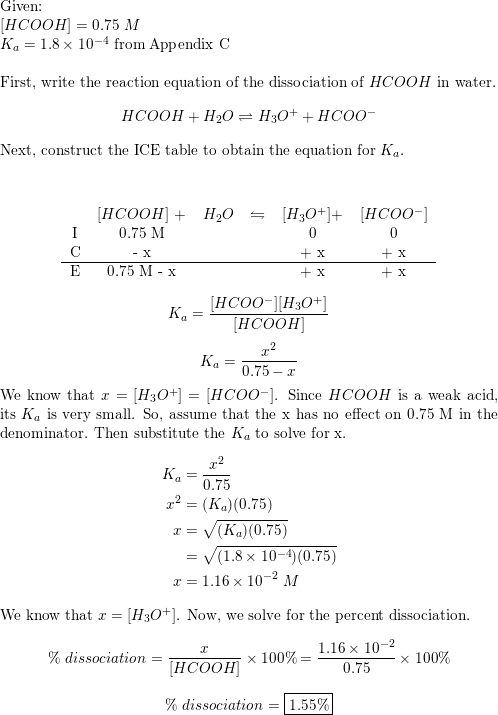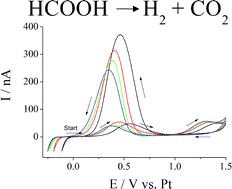
Clean, efficient electrolysis of formic acid via formation of eutectic, ionic mixtures with ammonium formate - Energy & Environmental Science (RSC Publishing)

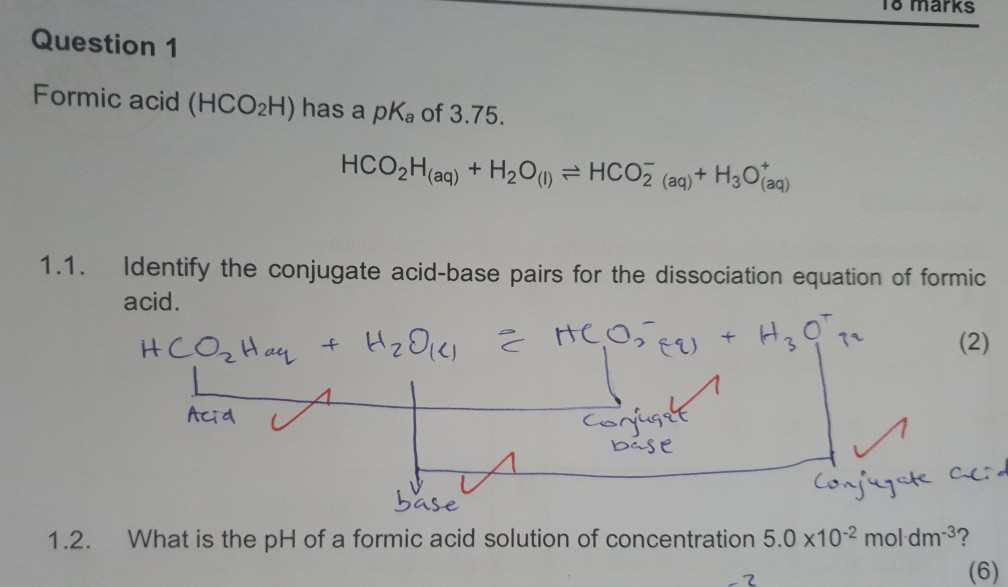
SOLVED: Formic acid dissociates in water according to the equation: HCOOH(aq) HO() H;O (aq) HCOO (aq) Given the following equilibrium concentrations; calculate the equilibrium constant: IHCOOHI = 0.550 M, [o [ =

Acid Dissociation Constant. Dissociation Constants For a generalized acid dissociation, the equilibrium expression would be This equilibrium constant. - ppt download
The self-ionization constant for pure formic acid, K = [HCOOH2+] [HCOO–] has been estimated as 10–6 at room temperature. What percentage of formic acid molecules in pure formic acid are converted to

Problem : What percent of formic acid (HCOOH) is dissociated in a 0.1 M solution of formic acid? The K a of formic acid is 1.77 x 10-4. | By Kurse Shkencore | Facebook

Formic acid dimer dissociation enthalpy as a function of temperature... | Download Scientific Diagram
![Weak Acids & Bases Chapter 16. Dissociation Constants Since weak acids do not dissociate completely, [H 3 O + ] ≠ [acid] For a generalized acid dissociation, - ppt download Weak Acids & Bases Chapter 16. Dissociation Constants Since weak acids do not dissociate completely, [H 3 O + ] ≠ [acid] For a generalized acid dissociation, - ppt download](https://images.slideplayer.com/33/9517443/slides/slide_4.jpg)
Weak Acids & Bases Chapter 16. Dissociation Constants Since weak acids do not dissociate completely, [H 3 O + ] ≠ [acid] For a generalized acid dissociation, - ppt download

Question Video: Calculating the Concentration of H3O+ Ions in an Aqueous Solution of Formic Acid | Nagwa

Acids at the Edge: Why Nitric and Formic Acid Dissociations at Air–Water Interfaces Depend on Depth and on Interface Specific Area | Journal of the American Chemical Society
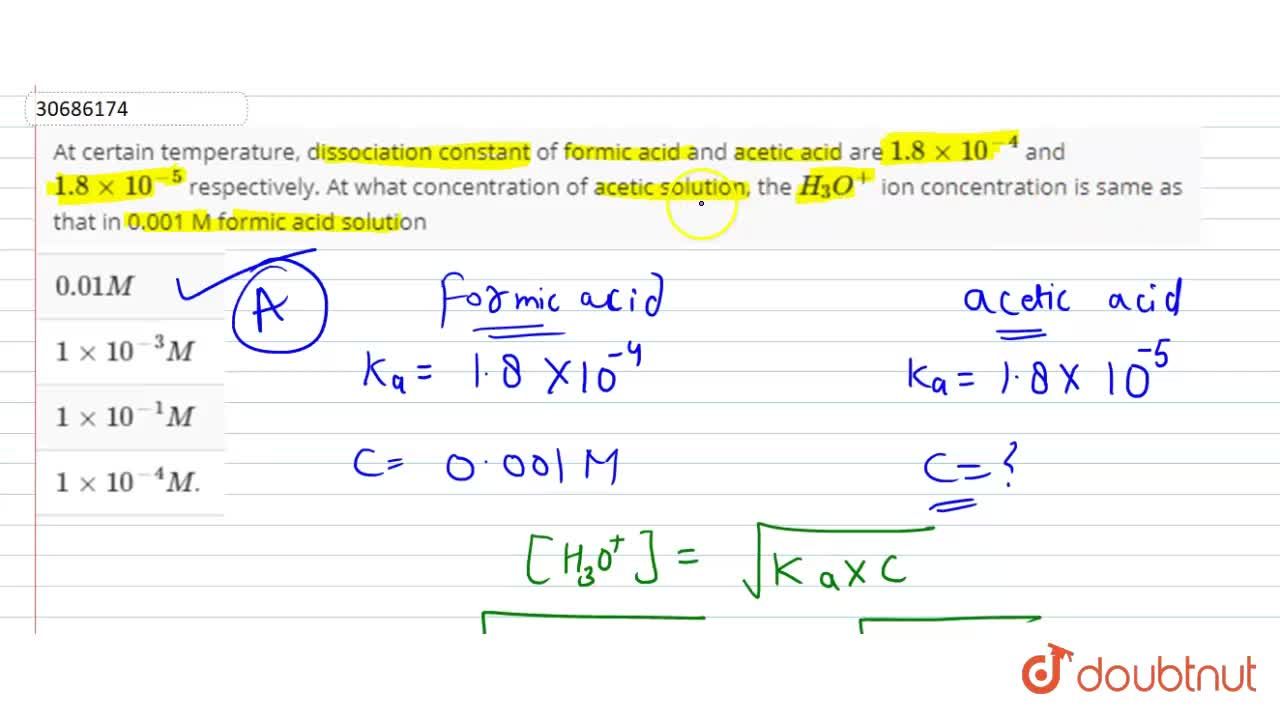
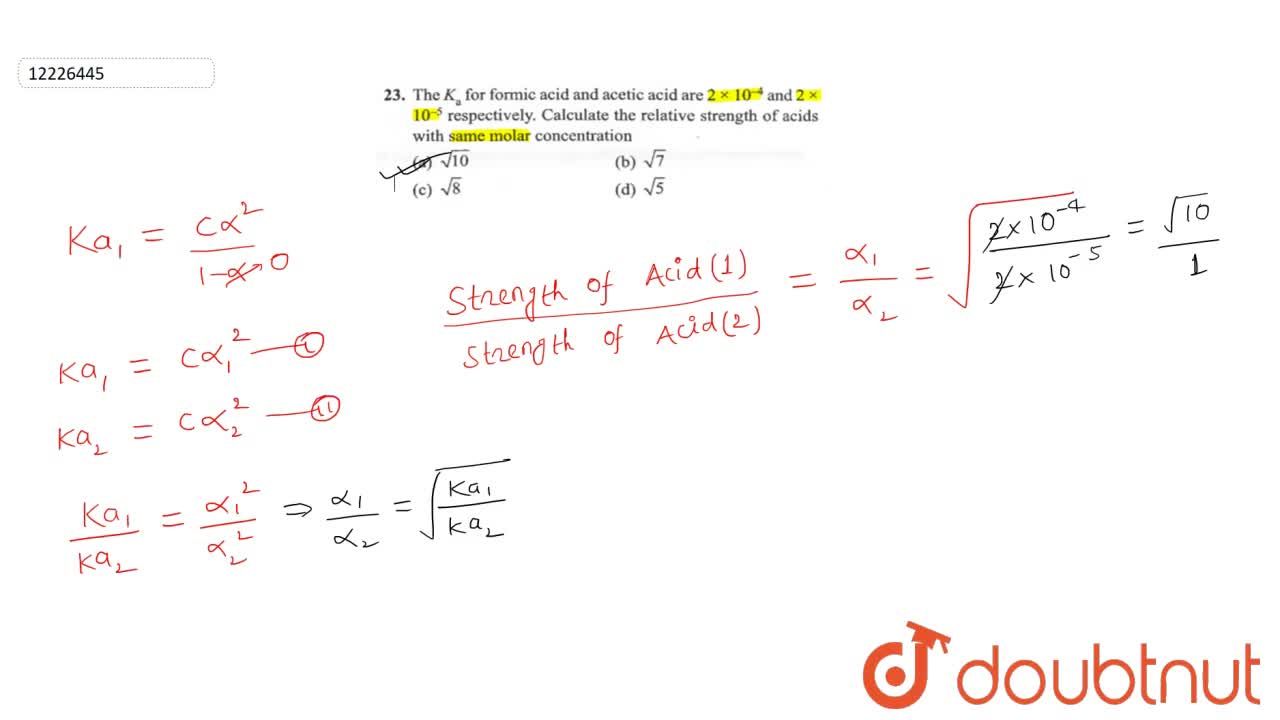
At certain temperature, dissociation constant of formic acid and acetic acid are 1.8xx10^(-4) and 1.8xx10^(-5) respectively. At what concentration of acetic solution, the H93)O^(+) ion concentration is same as that in 0.001
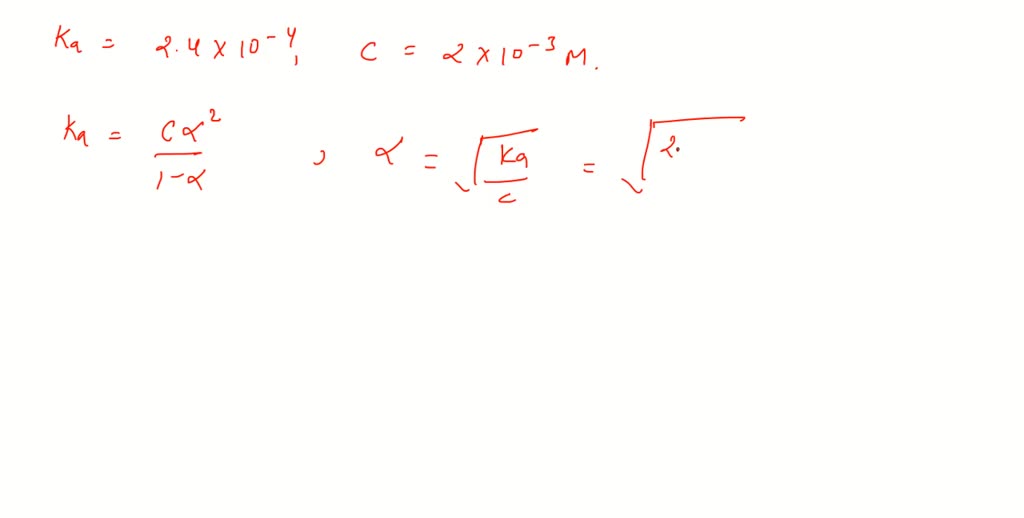
SOLVED:The dissociation constant of formic acid is 0.00024. The hydrogen ion concentration in 0.002 M-HCOOH solution is nearly (a) 6.93 ×10^-4 M (b) 4.8 ×10^-7 M (c) 5.8 ×10^-4 M (d) 1.4 ×10^-4 M
![The self - ionization Constant for pure formic acid, K = [HCOOH2^+][HCOO^-] has been estimated as 10^-6 M^2 and the density of formic acid is 1.22 g/cm^3 at room temperature. If 'x The self - ionization Constant for pure formic acid, K = [HCOOH2^+][HCOO^-] has been estimated as 10^-6 M^2 and the density of formic acid is 1.22 g/cm^3 at room temperature. If 'x](https://haygot.s3.amazonaws.com/questions/1751876_1682314_ans_b5d65e461d6e4d78995f4f598ca7ec65.png)
The self - ionization Constant for pure formic acid, K = [HCOOH2^+][HCOO^-] has been estimated as 10^-6 M^2 and the density of formic acid is 1.22 g/cm^3 at room temperature. If 'x
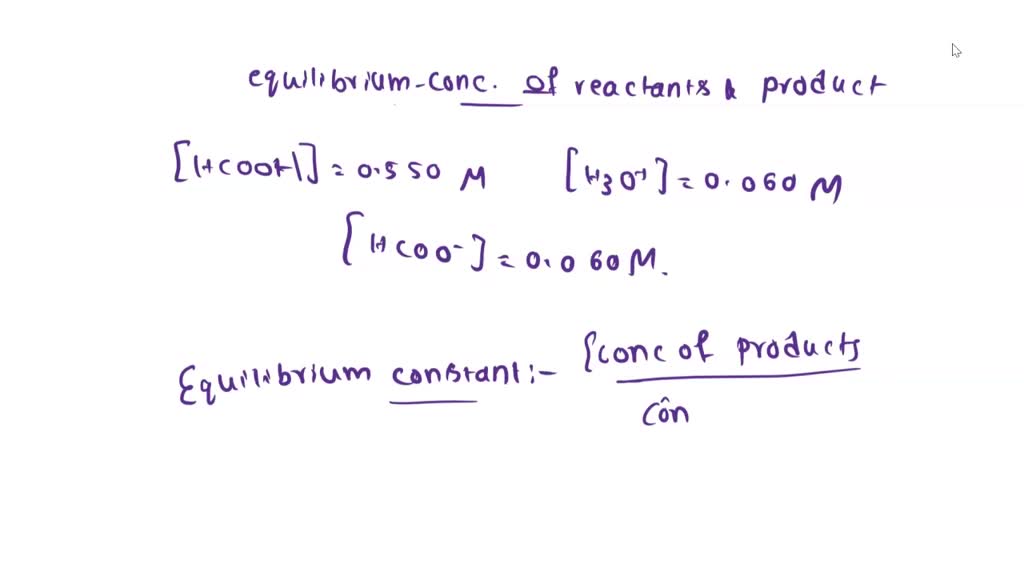
SOLVED: Formic acid dissociates in water according to the equation: HCOOH(aq) HO() H;O (aq) HCOO (aq) Given the following equilibrium concentrations; calculate the equilibrium constant: IHCOOHI = 0.550 M, [o [ =